How to interact with the data in VR
Sitting or standing?
If you are new to VR when you start using iDaVIE-v we share here some tips on how to get confortable while using VR:
You don’t have to stand. For long use we suggest you sit while ensuring there is enough room to freely move the controllers without crushing
You can walk around the data or move the data towards/around you while confortably sitting.
We developed the software with care to avoid risks related to motion sickness so we don’t expect problems with this. Nevertheless, if you never use VR before we suggest you start by moving slowly in the VR environment in order to get use to the new persepctive.
How to use the controllers
In this section we provide guidelines on how to use the Oculus controllers as this is our testing scenario. We can provide guidelines upon request on how to use e.g. VIVE controllers instead.
Tip
When setting up the VR system you can choose which hand is your “primary hand” you will use to deliver commands. This can also be set using the iDaVIE-v Main Menu in the VR GUI. Usually righ-handed people will set the right hand to be the primary hand and the left hand to be the secondary hand. The viceversa usually applies to left-handed people. In the following we will describe both scenarios and will refer to primary hand and secondary hands in this sense.
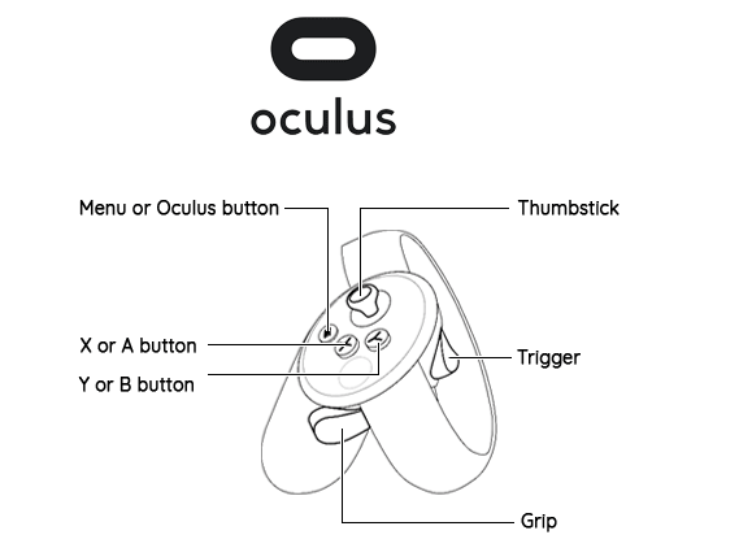
Thumbstick (primary hand): it can be used to scroll (up and down) lists (aka catalogs)
Thumbstick (secondary hand): it can be used to undo/redo a painting action (when in paint mode) by moving left (to undo) and right (to redo after undoing).
Menu button: this should NOT be pressed, it is a Oculus function unrelated to our software
Grip button: For navigation. Hold button down with one hand, this ‘grabs’ the cube, and you can move it around with hand/arm motion; press grip button on both hands to zoom in and out (arm motion in/out along horizontal axis), and rotation (hand/arm motion that is a scissor motion).
“Y” or “B” button: it activates the quick menu option (see Graphical User Interface). If the primary hand is set to be the left hand then the reference button is the “Y” button; if the primary hand is set to be the right hand then the reference button is the “B” button.
“X” or “A” button: it activates the seclection option. Use this to create a box around a region (e.g. a source) of choice. How to use this: you reach your hand behind and upward of the object (in 3D), press and hold button as you drag it across and down the source, creating a box within which your regiond of interest should be. After you have selected the source, you can crop the box using either a voice command “Crop Selection” or the Crop button in the Quick Menu. If the primary hand is set to be the left hand then the reference button is the “X” button; if the primary hand is set to be the right hand then the reference button is the “A” button.
Trigger: it is used for a number of actions:
once a menu is active a laser pointer will be visible. The trigger can then be used to select options on menus.
when the voice command “Edit min” or “Edit max” or “edit z* axis” (see section Voice commands) are activated, the user can change the min/max thresholds or tune the z-axis,by moving up/down or right/left the primary hand respectively. In both cases, when the user is happy with the new threshold or z-axis can use the trigger to save the new configuration.
Voice commands
In VR the use of the controllers can become tricky so we have implemented a series of voice commands that can be used as an alternative to interact with the data. The list below contains all the possible voice commands that can be used in alternative to the options in the VR quick menu. Each of the following commands will have the exact same outcome as the menu actions. A vocal command is activated once the user receive an haptic feedback (vibration) on the main hand controller. If no feeback is received than the voice command did not activate and the user should try again.
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
Changing voxel thresholds |
|
“Edit min” |
to set the minimum threshold (floor) of the voxel intensity mapping |
“Edit max” |
to set the maximum threshold (cieling) of the voxel intensity mapping |
“Reset threshold” |
to reset the thresholding to the default (startup) values |
Changing color map |
|
“color map plasma” |
to set the color map to a favourite one. Options are: plasma, turbo, rainbow, magma, inferno, viridi, cube helix |
“reset tranform” |
to reset the color mapping to the default magma color map |
Changing ray marching settings |
|
“projection maximum” |
(DEAFULT) ray-marching with maximum voxel intensity |
“projection average” |
ray-marching with average along line-of-sight |
Changing voxels scale |
|
“linear scale” |
(DEAFULT) voxel values are displaied in linear scale |
“log scale” |
voxel values are displaied in log scale |
“square root scale” |
voxel values are displaied in sqaure root scale |
Changing cube size scaling |
|
“edit zee axis” or “edit zed Axis” |
to edit the z-axis of the cube (e.g. to compress the cube to a single layer or strech it). NOTE: by doing this action no beam convolution is taken into account. We assume that every channel has the same beam size. Only in the Beta release there will be the opportunity to create a moment-0 map of the cube.and thus a proper convolution will be done (if different channels have different beams). |
“save zee axis” or “save zed Axis” |
to save the new z axis scale |
“reset zee Axis” or “reset zed Axis” |
to reset the z-axis to the default (startup) values |
Selecting regions of interest |
|
“crop selection” |
after selecting an object/region of interest using the controllers this command will crop the region within the box from the full cube and will render it at full resolution (depending on the dimension of the selected region) |
“reset crop” |
to return to the full cube view |
Visualisation of cube masks |
|
“mask on” |
if a cube mask is loaded this command will allow to visualise only those voxels that belong to the mask |
“mask off” |
to turn off the mask visualisation |
“mask invert” |
opposite of mask on; to show anything that is not in a mask or, in other words, to show the “residuals” (cube - mask cube); usefull to find new sources |
“mask isolate” |
to light up the masked voxels; use to easily see mask |
Painting options |
|
“paint mode” |
to activate the paint mode where the user can modify/create a mask |
“exit paint mode” |
to exit the paint mode |
“brush add” |
to add voxels to a mask |
“brush erase” |
to delete voxels of a mask |
“show mask outline” |
to show the mask outline as a transparent grid (DEFAULT: the mask outline will be authomatically set when in paint mode) |
“hide mask outline” |
to hide the mask outline as a transparent grid |
“undo” |
undo a paint mode action |
“redo” |
redo a paint mode action |
“add new source” |
to specify the user is now adding a new source to the mask |
“set source ID” |
to set the mask voxels the user is about to paint to the value of a specific source ID. In this way the software will recognize the voxels as part of a specific source indicated and not as a new source. |
Screenshot options |
|
“take picture” |
to take a screenshot of what is in front of the user in VR. The screenshot taken will then be authomatically saved as a .png file in |
Catalog actions |
|
“teleport” |
when a source is selected in a list this command will teleport the user at the position of the source in the cube |
Get cursor information |
|
“cursor info” |
to visualise any info available for the voxel where the cursor is. Default information are WCS,v_rad, volume value, voxel value in the Units of the cube, Frequency (if stored in the header), source ID (if a mask is loaded). |
Note
We are aware that the voice commands do not work when the user is recording a movie using an external software. In this case the user should use the menu options. See more in the section “How to” demos.